Faminesindia
Thursday, October 9, 2025
Great famine 1876
Sunday, October 5, 2025
Timeline of major famines in India during British rule
The timeline of major famines in India during British rule covers major famines on the Indian subcontinent from 1765 to 1947. The famines included here occurred both in the princely states (regions administered by Indian rulers), British India (regions administered either by the British East India Company from 1765 to 1857; or by the British Crown, in the British Raj, from 1858 to 1947) and Indian territories independent of British rule such as the Maratha Empire
Indian famine of 1896–1897
drawing, titled "Famine in India," from The Graphic, February 27, 1897, showing a bazaar scene in India with shoppers, many of whom are emaciated, buying grain from a merchant's shop
Indian famine of 1899–1900
Famines relief 1901
The Indian famine of 1899–1900 began with the failure of the summer monsoons in 1899 over Western and Central India and, during the next year, affected an area of 476,000 square miles (1,230,000 km2) and a population of 59.5 million.[1] The famine was acute in the Central Provinces and Berar, the Bombay Presidency, the minor province of Ajmer-Merwara, and the Hissar District of the Punjab; it also caused great distress in the princely states of the Rajputana Agency, the Central India Agency, Hyderabad and the Kathiawar Agency.[1] In addition, small areas of the Bengal Presidency, the Madras Presidency and the North-Western Provinces were acutely afflicted by the famine.[1
Ancient, medieval and pre-colonial
One of the earliest treatises on famine relief goes back more than 2,000 years. This treatise is commonly attributed to Kautilya who was also known as Vishnugupta (Chanakya), who recommended that a good king should build new forts and water-works and share his provisions with the people, or entrust the country to another king.[10] Historically, Indian rulers have employed several methods of famine relief. Some of these were direct, such as initiating free distribution of food grains and throwing open grain stores and kitchens to the people. Other measures were monetary policies such as remission of revenue, remission of taxes, an increase of pay to soldiers, and payment of advances. Yet other measures included the construction of public works, canals, and embankments, and sinking wells. Migration was encouraged.[10] Kautilya advocated raiding the provisions of the rich in times of famine to "thin them by exacting excess revenue."[5] Information on famines from ancient India up to colonial times is found in five primary sources:[11]
Legendary accounts passed down in oral tradition that keep alive the memory of famines
Ancient Indian sacred literature such as the Vedas, Jataka stories, and the Arthashastra
Stone and metal inscriptions provide information on several famines before the 16th century
Writings of Indian historians in Mughal India
Writings of foreigners temporarily resident in India (e.g. Ibn Battuta, Francis Xavier)
The ancient Ashokan edicts of the Mauryan age around 269 BCE record emperor Asoka's conquest of Kalinga, roughly the modern state of Odisha. The major rock and pillar edicts mention the massive human toll of about 100,000 due to the war. The edicts record that an even larger number later perished, presumably from wounds and famine.[12] From Indian literature, there is the 7th-century famine due to failure of rains in Thanjavur district mentioned in the Periya Puranam. According to the Purana, Lord Shiva helped the Tamil saints Sambandar and Appar to provide relief from the famine.[13] Another famine in the same district is recorded on an inscription with details such as "times becoming bad", a village being ruined, and cultivation of food being disrupted in Landing in 1054. [14]
Famines preserved only in oral tradition are the Dvadasavarsha Panjam (Twelve-year Famine) of south India and the Durga Devi Famine of the Deccan from 1396 to 1407.The Vanjari story of the great Durgadevi famine, which lasted from 1396 to 1407, is that it was named from Durga a Lad Vanjari woman, who had amassed great wealth and owned a million pack bullocks, which she used in bringing grain from Nepal, Burmah, and China.
She distributed the grain among the starving people and gained the honourable title of ' Mother of the World, Jagachi Mata..[13][15] The primary sources for famines in this period are incomplete and locationally based.[13]
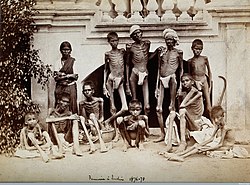





.jpg)
